The National Rural Health Mission (NRHM) was launched by the Government of India on 12 April 2005 to carry out a necessary architectural correction in the basic healthcare delivery system and thus provide comprehensive integrated health care to rural people, especially the vulnerable sections of the society, namely, women and children1.
One of the key strategies under the NRHM is having a community health worker who is an Accredited Social Health Activist (ASHA) for every village with a population of 1000. These ASHA workers should preferably be female, in the 25-45 years age group and have a qualification of at least eighth class2.
Accredited Social Health Activists have to undergo a series of modular training programs at the district hospitals / Block Primary Health Centres (PHCs) by the trained Taluka medical officer / district health officer. The ASHAs receive performance-based incentives for promoting universal immunization, referral and escort services for reproductive and child health (RCH) and other healthcare programs3.
With the introduction of ASHA workers under the NRHM from 2005 to 2006 in India, utilization of healthcare services at the peripheral level has improved4. Accredited Social Health Activist workers are supposed to increase the health awareness among women and also add to the resources of the health department4. According to a report released by the State Institute of Health & Family Welfare, Rajasthan, ASHA workers have brought an increase of 80.7% in institutional deliveries5. Research conducted in rural North India investigated contextual features of the program that hinder the ASHAs' capacity to increase quantitative health outcomes and found that ASHAs were institutionally limited by the outcome-based remuneration structure and poor institutional support6.
The basic rationale for conducting this study was to evaluate knowledge, attitudes and practices of ASHA workers in relation to child health so that proper interventions in the form of refresher training sessions could be undertaken to improve their knowledge in any deficient fields. Also, this study will help program managers in formalizing the future training sessions of newly recruited ASHA workers so they can focus on areas in which a knowledge-practice gap is identified.
A cross-sectional study was conducted at Palghar Taluka in the Thane district of Maharashtra, India for a period of 3 months from January 2011 to March 2011, inclusive, with the study participants all being trained ASHA workers working in the various primary health centres of Palghar Taluka. A total of 150 ASHA workers were working in the area, of which four workers were untrained and thus excluded from study.
The study was conducted by the authors after gaining permission from the medical officer in charge of the primary health centres, who introduced the authors to the ASHA workers at the time of their monthly meetings and also helped the authors to achieve rapport with the ASHA workers. A pre-tested, semi-structured questionnaire was designed for ASHA workers regarding child health after thoroughly studying the ASHA Training Module 2, which was then translated into the workers' local language (ie Marathi)7. Each of the ASHA workers was then contacted individually by the authors and after having the aim of the study explained, was interviewed face to face using the semi-structured questionnaire. Informed consent was taken from each of the study participants.
Each of the study participants was assured by the authors that the study findings would not have any impact on their job. The data were analyzed using SPSS v17 (www.spss.com).
Ethics approval
The Committee for Academic Research Ethics approved the study (#997/2010).
All of the ASHAs belonged to the local community and acted as effective link people in the delivery of health services and in providing health awareness. All of the study participants displayed the correct knowledge about advising pregnant women and their families regarding institutional deliveries; knew the correct advice regarding registration of birth; displayed correct knowledge regarding advising woman to undergo a minimum of three post-natal check-ups; and displayed correct knowledge regarding counselling exclusive breastfeeding for newborns.
It was also observed that 67 ASHA (45.9%) workers referred lactating mothers with complaints such as sore or cracked nipples or foul-smelling discharge from nipples to hospital, while 54 (37%) incorrectly advised breast massage with oil to the mothers. The oral contraceptive pill was the most commonly advised contraceptive measure, followed by an intrauterine device.
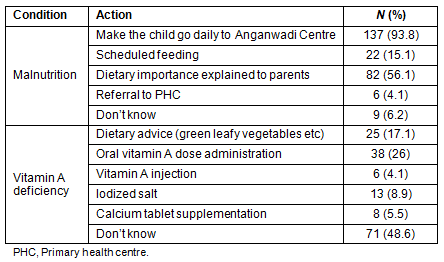
The socio-demographic profile of the ASHA workers is provided (Table 1). Out of the total 146 ASHA workers, 70 (47.9%) were below the age of 25 years. The minimum age of the ASHA worker was 17 years and the maximum age was 34 years. Sixty-seven (45.9%) of the ASHAs were educated below a secondary school level.
The ASHA workers' knowledge regarding danger signals in children requiring urgent referral is provided (Table 2). It was observed that despite training, 29 ASHAs (19.9%) did not feel the need to refer a child with diarrhoea who is unable to drink or breast feed. Similarly, in acute respiratory tract infections, 35 ASHAs (23.9%) did not know to refer a child with fast breathing. A total of 59 ASHAs (40.4%) considered a baby crying for more than 3 hours following immunization not worth referring to a first referral unit.
The preventive actions taken by the ASHAs for malnutrition and vitamin A deficiency is provided (Table 3). Only nine ASHAs (6.2%) did not know what to do for malnourished children. Though all ASHA workers were giving vitamin A as part of the immunization schedule, 71 ASHAs (48.6%) were unaware of preventive actions to be taken for Vitamin A.
Table 1: Distribution of Accredited Social Health Activist
workers according to sociodemographic parameters
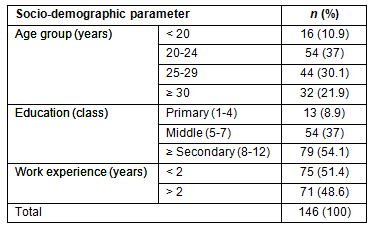
Table 2: Accredited Social Health Activist workers' knowledge of danger
signals that indicate the need for immediate referral to a first referral unit
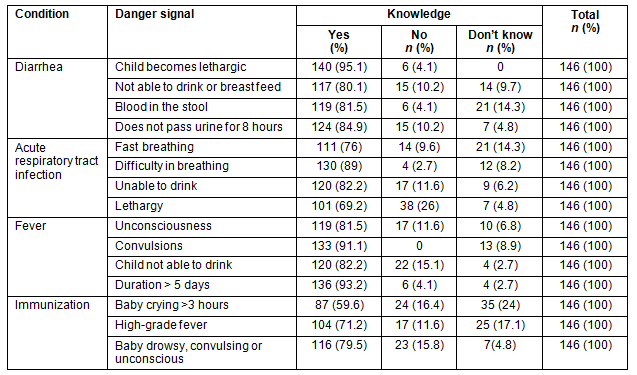
Table 3: Preventive actions taken for malnutrition and vitamin A deficiency
Discussion
All of the ASHAs belonged to the local community and acted as effective link people in the delivery of health services and in providing health awareness. In the present study, it was found that approximately 50% of the ASHA workers were below the age of 25 years, contrary to the fact that as per guidelines, ASHAs should be in the 25-45 years age group2. Also, 67 (45.9%) of the ASHAs were educated below a secondary school level despite the requirement that ASHAs be educated to at least an 8th class standard2. In a study conducted in Surendranagar, 70% of the ASHAs had an education level that was between the 8th and 12th class, while in the present study it was approximately 54.1%8. Probable reasons could be low levels of literacy in the local area and a non-availability of educated women.
In the current study, 100% correct knowledge was observed regarding giving advice to pregnant women and their families about promoting institutional deliveries and accompanying pregnant women at the time of delivery. In contrast to this, in a rapid appraisal of the ASHA scheme in Uttar Pradesh, it was observed that 70% of institutional deliveries were motivated and facilitated by the ASHAs9. In a study carried out in Surendranagar, it was found that 86% of ASHAs were conducting improper practice as they had poor knowledge regarding immediate referral condition8, while in the present study it was observed that in acute respiratory tract infections, 35 ASHAs (23.9%) did not know to refer a child with fast breathing.
In the present study, 100% of the ASHAs helped Auxiliary Nurse Midwives (ANMs) in mobilizing beneficiaries at immunization sites, while in a study conducted in Gujarat, only 11.4% of the healthcare workers were working as mobilizers for immunization sessions10. Also, in a study conducted in Uttar Pradesh, 59% of the immunization activities were facilitated by ASHA workers9.
In a study conducted in Jharkhand, it was observed that only 5.7% of the study participants promoted community members to receive Integrated Child Development Services (ICDS) facilities from Anganwadi Centre, while in the present study 93.8% of ASHA workers advised parents of malnourished children to take them daily to the Anganwadi Centre11.
In a study carried out in Orissa, approximately 78.9% of the beneficiaries of the Janani Suraksha Yojana (JSY) service said that ASHA workers prompted them to use the service12. In the current study, 100% of the ASHA workers displayed correct knowledge about the JSY service.
In a study undertaken in Rajasthan, it was observed that only 25% of the ASHA workers were aware of their responsibilities in helping ANM in the immunization program13, while in the present study almost 100% of ASHA workers were actually helping other healthcare staff in carrying out immunization services. In the Rapid Assessment of Communitization Processes of the National Rural Health Mission in Orissa, it was revealed that ASHAs felt that advising pregnant women on an institutional delivery was part of their prime agenda and they had not failed in that aspect14.
In the present study, 100% correct knowledge was observed regarding counselling the exclusive breastfeeding of newborns. In contrast to this, in a study conducted in Orissa it was observed that 81.3% of ASHA workers had knowledge about their responsibilities regarding counselling on antenatal care/ postnatal care, breastfeeding and immunization15. The current study had its limitations in that the quality of the training that the ASHA workers had received was not assessed and the possibility of recall bias cannot be ruled out.
Despite the training given to ASHA workers, lacunae still persists in their knowledge regarding various aspects of 'child morbidity and mortality'. Training is the backbone of capacity building and functioning of ASHAs. Thus, it must be timely, proper and effective. It should be ensured during training that ASHAs are well aware of their job responsibilities. Monthly meetings should be used as a platform for regular reinforcement of various aspects of child health. In training sessions, more emphasis should be given to danger signals requiring referral and conceptual understanding of the reasons behind vitamin A supplementation.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the medical officers in charge of the various primary health centres for giving them the permission to conduct the study.
References
1. Government of India. National Rural Health Mission (2005-2012) Mission Document. New Delhi: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, 2005.
2. Government of India. NRHM-ASHA (2005) Guidelines. New Delhi: Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, 2005.
3. Ministry of Health & Family Welfare. National rural health mission PIP: 2011-12; Mission flexipool. (Online) no date. Available: http://pipnrhm-mohfw.nic.in/index_files/non_high_focus_large/maharastra/NRHMFlexipool&Immunazation.pdf (Accessed 30 January 2012).
4. Ministry of Health & Family Welfare. About ASHA. (Online) 2006. Available: http://www.mohfw.nic.in/NRHM/asha.htm (Accessed 4 February 2012).
5. State Institute of Health & Family Welfare, Jaipur. Accredited Social Health Activist (ASHA). (Online) 2008. Available: http://www.sihfwrajasthan.com/ppts/full/ASHA.pdf (Accessed 2 February 2012).
6. Scott K, Shanker S. Tying their hands? Institutional obstacles to the success of the ASHA community health worker programme in rural north India. AIDS Care 2010; 22(2Suppl): S1606-S1612.
7. Ministry of Health & Family Welfare. ASHA Manual Book 2. (Online) 2006. Available: http://www.mohfw.nic.in/NRHM/Documents/ASHA_Book_No_2.pdf (Accessed 12 January 2012).
8. Mahyavanshi DK, Patel MG, Kartha G, Purani SK, Nagar SS. A cross sectional study of the knowledge, attitude and practice of ASHA workers regarding child health (under five years of age) in Surendranagar district. Healthline 2011; 2(2): 50.
9. Jain N, Srivastava NK, Khan AM, Dhar N, Adhish V, Menon S et al. Assessment of the functioning of ASHAs under NRHM in Uttar Pradesh. Health and Population: Perspectives and Issues 2008; 31(2): 132-140.
10. Patel T, Raval D, Pandit N. Process evaluation of routine immunization in rural areas of Anand District of Gujarat. Healthline 2011; 2(1): 17.
11. Haider S, Adhish SV, Gupta S, Dhar N, Datta U, Menon S et al. A rapid appraisal of SAHIYA (ASHA) in Jharkhand. Health and Population: Perspectives and Issues 2008; 31(2): 80-84.
12. Mohapatra B, Datta U, Gupta S, Tiwari VK, Nair KS, Adhish V et al. An assessment of the functioning and impact of Janani Suraksha Yojana in Orissa. Health and Population: Perspectives and Issues 2008; 31(2): 120-125.
13. Uttekar BP, Barge S, Khan W, Deshpande Y, Uttekar V, Sharma J et al. Assessment of ASHA and Janani Suraksha Yojana in Rajasthan. (Online) 2008. Available: http://nihfw.org/pdf/RAHI-I%20Reports/Orissa/ORISSA.pdf (Accessed on 24 December 2011).
14. Public Health Resource Society, New Delhi. A rapid assessment of communitization processes of the National Rural Health Mission in Jharkhand, Orissa and Bihar: Jan-Mar 2009. New Delhi: Public Health Resource Society, 2009.
15. Swain S, Swain P, Nair KS, Dhar N, Gupta S, Nandan D. A rapid appraisal of functioning of ASHA under NRHM in Orissa. Health and Population: Perspectives and Issues 2008; 31(2): 73-79.

