Introduction
Gay, bisexual, and other men who have sex with men (GBMSM), transgender, and gender-expansive populations are disproportionately affected by HIV and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates a lifetime risk for HIV infection among GBMSM of one in six, compared with the risk among heterosexual men of 1 in 5241. In one CDC study, 42% of transgender women who were interviewed were found to be living with HIV2 and transgender women account for the vast majority of new HIV diagnoses among transgender people3. HIV testing is a key pillar of the Ending the HIV Epidemic initiative4 and provides a key point of entry to additional prevention services for those who test negative, and a key point of entry to treatment for those testing positive.
The geographic area of the US with the greatest incidence of HIV diagnoses is the South, which constitutes over half of new cases3. Rural residence is a risk factor for decreased rates of testing, later adoption of new treatments, and increased mortality from HIV5,6. In rural areas, 77% of new diagnoses are among GBMSM, and an additional 7% of diagnoses in rural areas are among GBMSM who also inject drugs7. Furthermore, those with HIV in rural areas face a lack of accessible transportation, lack of healthcare professionals who are adequately trained in HIV prevention and care, long distances to travel to care, and exacerbated effects of social determinants, stigma, and mental health conditions8-11.
Much of the focus on HIV prevention, care, and treatment has been centered on populations in urban areas because the prevalence of HIV is higher in urban counties than in rural counties12. However, many rural counties in the South have prevalence rates in the top decile in the country13. Furthermore, people in rural areas are more likely to have a late diagnosis of HIV, indicating that prevalence estimates in some rural areas likely underestimate the true disease burden14. Lack of knowledge of infection leads to increased morbidity, reduced survival, and increased opportunities for onward transmission15. The incidence of having AIDS upon diagnosis or within 1 year of diagnosis is significantly higher for rural residents compared with urban residents16,17.
CDC recommends HIV testing for GBMSM in the US at least annually, and acknowledges that testing every 3–6 months might be appropriate for those at higher risk. Although there are no recommendations specific to transgender people, CDC recommendations indicate that all people at risk should test at least annually18. Screening is essential for diagnosis, to begin antiretroviral treatment and other forms of care, and to enter into pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP) care for those testing negative and at increased risk. Yet, there are substantial disparities in testing comparing urban and rural GBMSM. In one study investigating lifetime HIV testing rates among young adults aged 18–25 years, the proportion having ever been tested was 66% for non-urban participants and 88% for urban participants19. Another study found that 70% of the GBMSM in the non-urban group had ever been tested for HIV compared with 91% and 88% of GBMSM in Seattle and Atlanta, respectively20. Similarly, 68% of rural GBMSM had ever tested for HIV compared with 78% of non-rural GBMSM21. In a more recent study, young male couples living in rural areas were less likely to have been tested for HIV than young male couples living in urban areas22. Data describing disparities in HIV testing by urbanicity are lacking for transgender and gender non-conforming populations.
Numerous factors affect one’s ability to get tested for HIV in rural areas including lack of access to a testing site, lack of knowledge about testing, and stigma23. Thirteen percent of GBMSM live in PrEP deserts, where they have no access to PrEP care within 30 minutes. Location in the South and lower urbanicity are associated with living in a PrEP desert10, and there is evidence that similar testing deserts might affect HIV testing uptake among rural SGM populations. Data from the Louisiana Department of Health found that, among 12 parishes in the rural north-eastern area of the state, there was one testing site available per 640.3 square miles (1658.4 km2) compared with the metropolitan area of New Orleans, which had one site for every 90.1 square miles (233.4 km2)24. The longer distance required to travel for HIV prevention and treatment services is a major barrier to care in rural areas.
Despite evidence for reduced access to HIV prevention services in rural areas, the independent association is not clear between distance and time required to travel to obtain a HIV test and lower prevalence of testing among rural compared with non-rural sexual and gender minority populations. Although time and distance traveled are inextricably linked, other factors, such as transportation mode (eg public versus private transport), can affect travel time, and it is unclear which of these factors has the greatest effect on HIV testing uptake. We sought to examine how access to testing locations affects the likelihood of recent or regular testing among GBMSM and transgender and other gender-expansive people in the rural South. The purpose of the present study is to evaluate the independent effects of distance and time travelled to a HIV/STI testing center on whether one was tested in the previous 12 months among sexual and gender minority populations in the rural South.
Methods
Study design and data collection
We conducted a cross-sectional survey of GBMSM and gender minority populations in the southern US from April 2021 to January 2022. Participants were recruited by online advertisements and email messages to participants from previous research studies who provided informed consent to be re-contacted. Notably, the previous research participants were also recruited using online advertisements on social and sexual networking sites and apps. Interested potential participants were directed to an online eligibility screening survey. Those who were eligible were then able to immediately provide electronic informed consent and take the study survey. Participants also had the option of receiving an email with a unique link to the survey that was valid for 2 weeks. Initially, participants were not compensated for their participation. However, in October 2021, we instituted a weekly raffle for a US$50 (A$77) electronic gift card. The raffle continued until recruitment ended in January 2022. We used IP addresses to ensure that each respondent was unique.
The study population consisted of individuals assigned male at birth who have sex with men or individuals assigned female at birth who are not cisgender women who have sex with men, are aged 18–34 years, and who live in the South region of the US as defined by the US Census Bureau. Participants were surveyed on demographics, sexual behavior in their lifetimes and in the past 6 months, access to health care, and HIV/STI testing history. Individual and structural factors were also collected. Of the 909 survey takers, 516 reported a history of HIV testing. Of those 516 respondents, eight were excluded for missing answers or responses of ‘don’t know’ or ‘prefer not to answer’ for the question of whether or not they received a HIV test in the previous 12 months. The final study sample included 508 participants who had reported receiving a HIV test in their lifetime.
Primary outcomes
Time since most recent test was assessed by asking participants if they had received a HIV test in the previous 12 months. Distance and time traveled to most recent test were assessed separately based on self-report. Responses for distance traveled were reported in miles and dichotomized as 20 miles (~32 km) or fewer versus more than 20 miles. Responses for time traveled were reported in minutes and dichotomized as 30 minutes or less versus more than 30 minutes.
Other measures
Participants also reported age, race/ethnicity (categorized as Hispanic, non-Hispanic Black, non-Hispanic white, or other/multiracial), education level (categorized as high school or less, some college, or college graduate or more), household income (categorized as US$0–19,999 (A$0–31,099), US$20,000–39,999 (A$31,100–62,199), US$40,000–74,999 (A$62,200–116,623), or US$75,000 (A$116,624) or more), insurance status (categorized as private, public, combination/other, or none), and condomless anal sex in the previous 6 months.
Rurality of residence was determined based on self-reported ZIP code, which was cross-walked to county using a standard algorithm25. Each county was then assigned a score using the Index of Relative Rurality, a continuous measure of rurality that ranges from 0.0 (most urban) to 1.0 (most rural)26. Counties with an Index of Relative Rurality of 0.4 or higher were categorized as rural, per the recommendations of the creators of the index. All other counties were categorized as non-rural. This method of classification has previously been shown to identify rural disparities in HIV prevention uptake21.
Data analyses
Stratified demographics were calculated and presented for both rural and non-rural subgroups. Poisson regression models with robust standard errors were used to estimate prevalence ratios for HIV testing in the previous 12 months. Unadjusted models were estimated for each of the demographic variables, distance traveled to most recent test, and time traveled to most recent test. Next, a single model was estimated with all covariates to determine adjusted prevalence ratios for time since most recent HIV test. The statistical software package SAS v9.4 (SAS Institute; https://www.sas.com) was used for all analyses.
Ethics approval
All study activities were reviewed and approved by the Emory University Institutional Review Board.
Results
Of the 508 participants included in the study, 155 (31%) lived in a rural area. The median age of the total study sample was 27 years (interquartile range 24–31 years). Nineteen percent (n=96) of participants identified as Hispanic, 22% (n=110) identified as non-Hispanic Black, 50% (n=252) identified as non-Hispanic White, and 9% (n=44) identified as another race or multiracial. Other demographic characteristics are shown in Table 1. Approximately half of participants were recruited from social and sexual networking sites and half from the pool of previous research participants.
Twenty-one percent (n=108) of participants were most recently tested for HIV more than 12 months prior to the survey: 24% (n=37) of rural participants and 20% (n=71) of non-rural participants (Table 2). Distance traveled to the most recent HIV test differed by rurality (p<0.0001). Fifteen percent (n=23) of rural participants traveled more than 20 miles (~32 km) to receive their most recent HIV test, but only 4% (n=14) of non-rural participants traveled over 20 miles for their most recent test. With respect to time traveled to most recent test, 16% (n=24) of rural participants and 13% (n=46) of non-rural participants traveled for more than 30 minutes for their most recent test.
In unadjusted analyses there was a statistically significant association between time since most recent test and distance traveled to test, race/ethnicity, and income (Table 3). Those who traveled more than 20 miles (~32 km) to their most recent test were 1.74 (95% confidence interval (CI) 1.09–2.80) times as likely to have not been tested in the previous 12 months compared with those who traveled 20 miles or less. Those who identified as Hispanic were 0.54 (95%CI 0.33–0.89) times as likely to have not been tested in the previous 12 months compared with those who identified as Non-Hispanic White. Those who identified as Non-Hispanic Black were 0.35 (95%CI 0.19–0.63) times as likely to have not been tested in the previous 12 months compared those who identified as Non-Hispanic White. Participants who reported an income level of US$0–19,999 (A$0–31,099) were 0.46 (95%CI 0.27–0.79) times as likely to have not been tested in the previous 12 months than those who reported an income level of US$75,000 (A$116,624) or more. Similarly, participants who reported an income level of US$20,000–39,999 (A$31,100–62,199) were 0.56 (95%CI 0.35–0.90) times as likely to have not been tested in the previous 12 months than those who reported an income level of US$75,000 (A$116,624) or more.
Statistically significant association between distance traveled to test, race/ethnicity, and income persisted in adjusted analyses. Those who had traveled more than 20 miles (~32 km) to their most recent HIV test were more than twice as likely to have not been tested in the previous 12 months (adjusted prevalence ratio (PR) 2.25, 95%CI 1.22–4.17). Non-Hispanic Black participants were less likely to have had their most recent HIV test more than 12 months prior to completing the survey (adjusted PR 0.36, 95%CI 0.18–0.70).
Table 1: Demographic and behavioral characteristics of sexual and gender minority survey respondents in the US South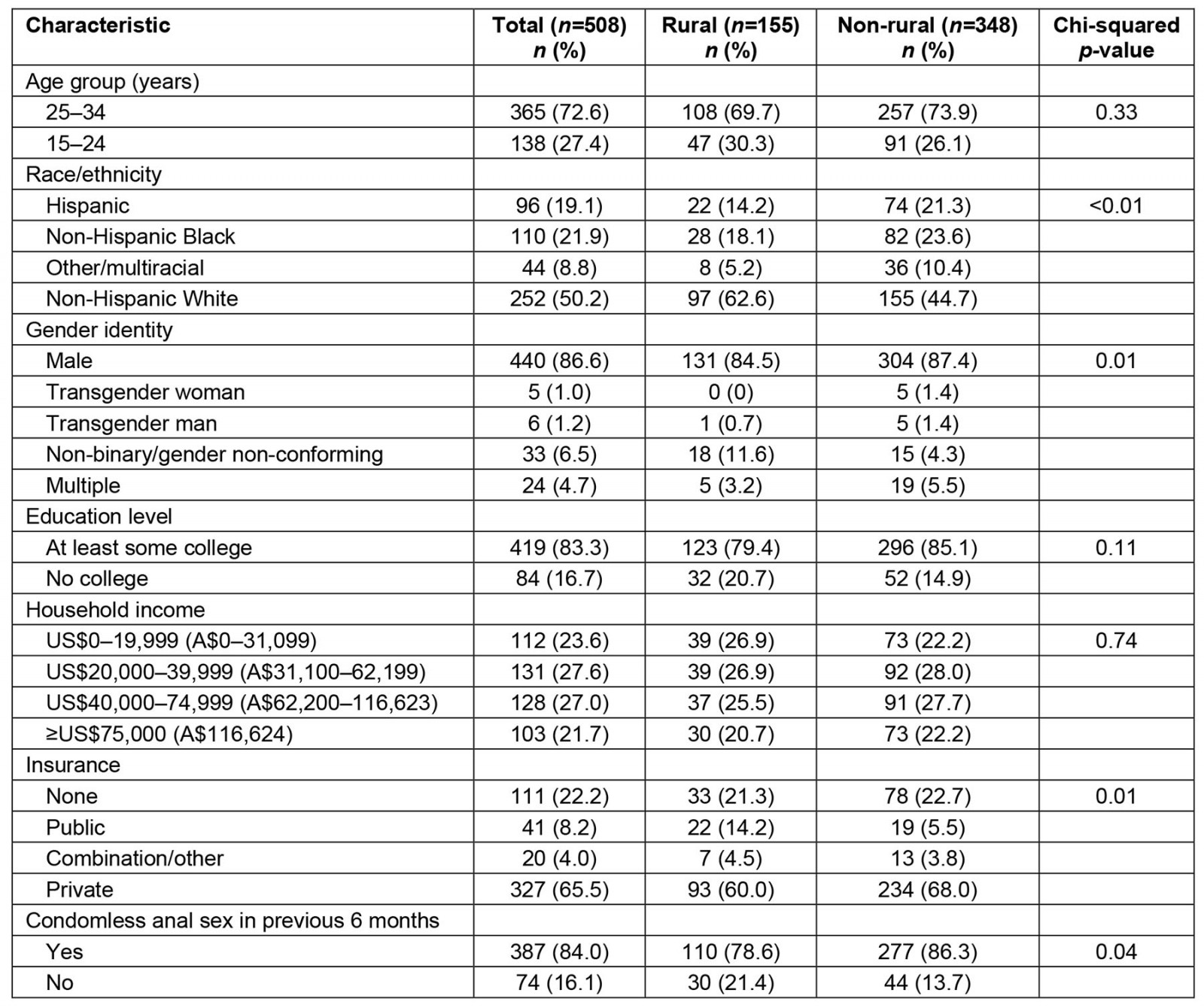
Table 2: Time since most recent HIV test, and distance and time traveled to most recent HIV test, among sexual and gender minority individuals in the US South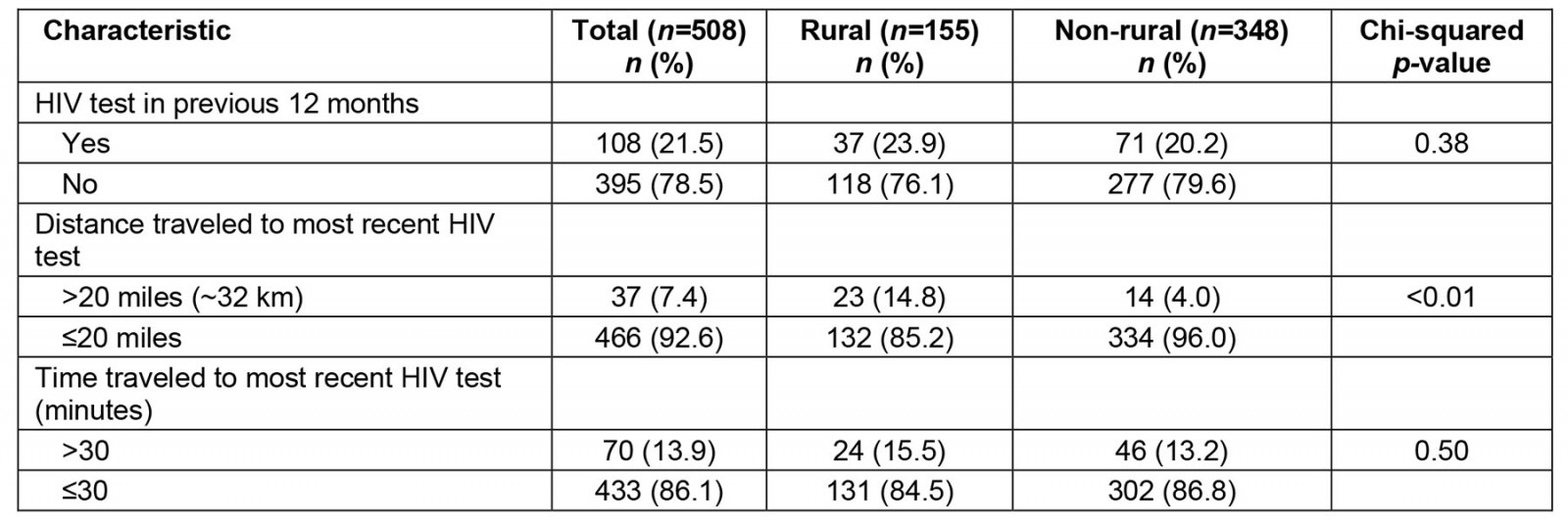
Table 3: Unadjusted and adjusted prevalence ratios for not receiving a HIV test in the previous 12 months among sexual and gender minority individuals in the US South who have ever had a HIV test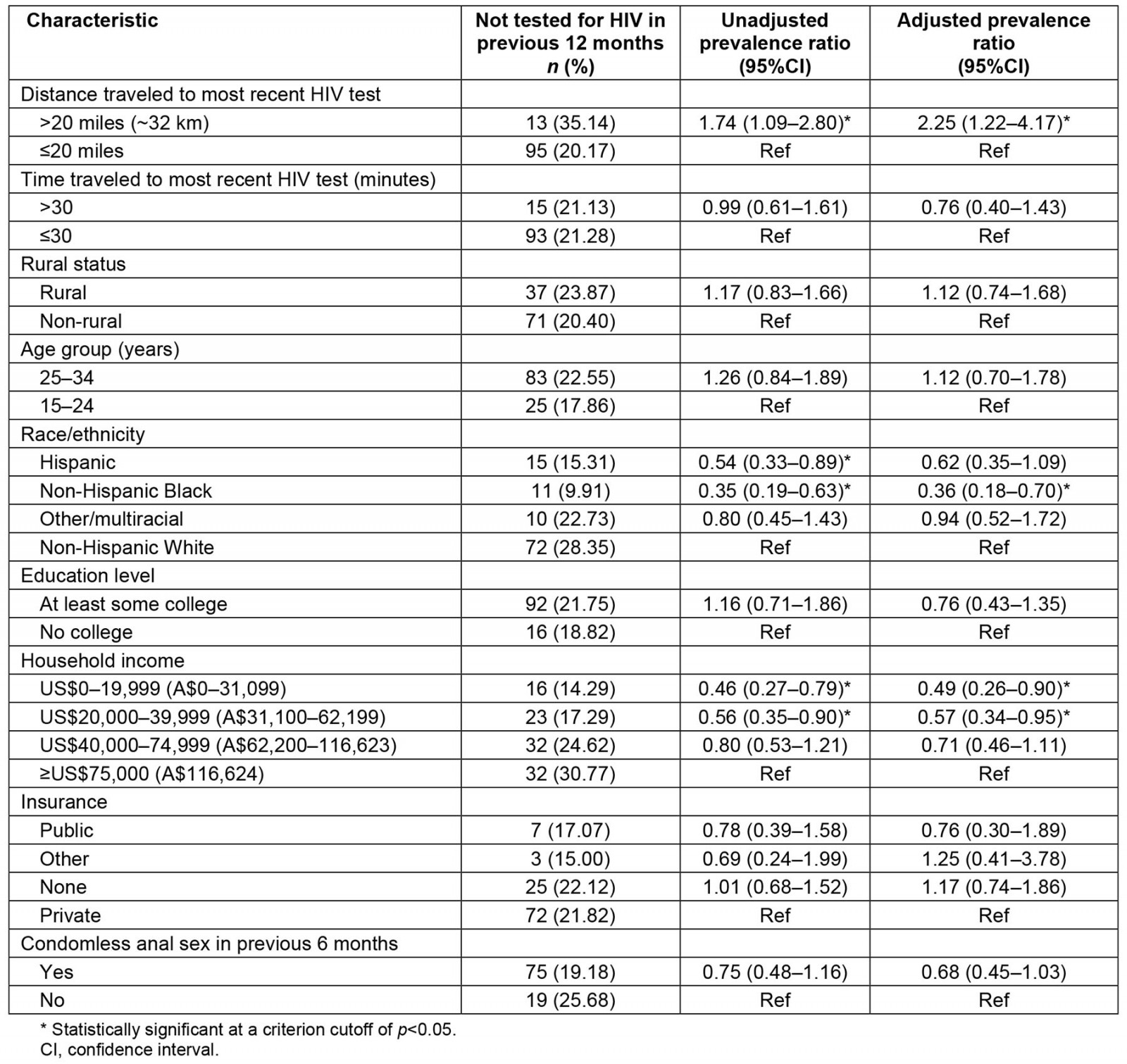
Discussion
We examined the associations between distance and time traveled to most recent HIV test with time since most recent HIV test among GBMSM and transgender people who have sex with men in the southern US. We found a significant positive association between traveling more than 20 miles (~32 km) to the most recent HIV test and not having a test in the previous 12 months but no association between time traveled to most recent HIV test and receiving a HIV test in the previous 12 months. These findings expand on prior research that suggests an association between traveling a longer distance to HIV testing sites and later diagnosis of HIV, as well as an association between distance from HIV testing sites and lower likelihood of getting tested for HIV27. Rural sexual and gender minority individuals face several challenges to accessing culturally competent sexual health care, and these results confirm that living in service deserts is independently associated with less frequent HIV testing.
Our finding that traveling a greater distance to receive the most recent HIV test is associated with a greater time since receiving the most recent test is consistent with past findings that people living further away from testing were less likely to be tested for HIV in Los Angeles, CA28. The present study looked at this association specifically among GBMSM and transgender people in the South due to the known disparities of HIV prevalence among GBMSM in the rural South3. This finding suggests that the distance required to travel to receive HIV screenings is a major barrier to testing in this population, even after controlling for other factors that may be associated with a lower likelihood of HIV testing. This finding is consistent with previous research that suggests living in areas with lower provider density, as is typical in rural areas10,24, results in reduced frequency of HIV testing. We controlled for condomless anal sex, so indications for testing did not confound the relationship.
We did not examine factors affecting distance traveled to the most recent HIV test. There may be no other testing sites available in the area or there may be limited access to closer sites due to financial, stigma, or privacy concerns29-31. Determining the cause of longer travel distance will help to determine the best strategies for mitigating this association. Future research should investigate the reasons that people need to travel long distances to access testing because this information will be necessary to develop interventions to reduce barriers. For example, it might be the case that there are no providers closer to their residence or it might be the case that people do not feel comfortable accessing HIV testing at providers located closer to their homes.
Our results indicate that rural residence is predictive of a longer time since most recent HIV test. This result is expected based on the results of overall testing rates of HIV being lower for rural populations than urban populations19,21. In the adjusted analysis, the association between rural residence and time since most recent test was attenuated somewhat. This suggests that distance traveled to receive HIV testing accounts for some, but not all, of the disparity in HIV testing uptake comparing rural and non-rural residents. Although we observed a strong association between distance traveled to most recent HIV test and time since most recent test, we did not observe a similar association between time traveled to most recent test and time since most recent test. We hypothesized that longer time traveled to the previous test would be associated with a longer time since last receiving a HIV test. It is possible that factors affecting travel time besides distance (eg traffic, use of public transportation) are not major deterrents to HIV testing uptake. Future research should investigate possible reasons why distance traveled, but not time, is associated with reduced recent HIV testing uptake.
Race and ethnicity are significantly associated with time since most recent HIV test. Hispanic and non-Hispanic Black participants were less likely to have not been tested for HIV in the past year compared with non-Hispanic White participants – independent of travel distance or income level. This result may be attributed to the increased focus on access to testing for these populations given the higher rates of HIV incidence these groups experience7.
We also found that lower income level – incomes of both US$0–19,999 (A$0–31,099) and US$20,000–39,999 (A$31,100–62,199) – were associated with more recent HIV testing times. This result is consistent with evidence that shows that young adults in the US with a non-functional income are more likely to report HIV testing than those with a functional income32. This relationship may be attributable to the increased HIV-prevention resources that are contributed to lower income populations. By contrast, qualitative evidence shows that rural MSM face exacerbated financial barriers including transportation costs, taking time off work, and co-pays for out-of-network clinics33. Future research should examine the relationship between increased barriers and increased outreach for lower income rural SGM populations.
Our results make clear that SGM people who live long distances from HIV testing providers need additional resources to overcome barriers to HIV testing. Telehealth and, specifically, at-home HIV testing services offer one option to increase testing among this population. HIV self-testing has consistently been demonstrated to be a feasible and acceptable method of HIV testing34-36. One qualitative study of rural cisgender MSM found high levels of support for at-home options for HIV and STI testing31. Future research should continue to investigate the use of HIV self-testing specifically among rural SGM populations, and any barriers to uptake that might be specific to these groups.
This analysis is subject to several limitations. These data are cross-sectional and based on self-report. We are comparing individuals who received their most recent HIV test within the previous 12 months and more than 12 months ago, so there might be differences in the accuracy of recall between the two groups. Another limitation is the sample size, specifically of the rural-residing cohort, decreasing the precision of our estimates. We were also unable to examine any differences in the testing experiences comparing GBMSM with transgender respondents.
This study yields important implications for access to testing in the rural South. GBMSM and transgender people traveling a further distance to access HIV testing are more likely to not have been tested in the previous 12 months, even though CDC recommends testing at least annually18. Improvements in access should be targeted toward individuals who do not live near testing sites, specifically in rural areas, and efforts should be made to increase the availability of HIV testing for rural residents, including using at-home self-testing35.
Conclusion
We observed a significant association between distance traveled to most recent HIV test and likelihood to have not been tested in the past year. These findings indicate a lack of access to HIV testing based on distance required to travel to a test and living in a rural area. Future work should further examine the factors affecting distance needed to travel to receive a HIV test and develop strategies to mitigate these factors.
Funding
This work was funded by the National Institute of Nursing Research (R56NR019482).
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.

