Introduction
Practising in remote community health centres can be challenging for healthcare professionals in dealing with medical emergencies, especially in areas where the resources are sparse and accessibility is limited. However, this provides an excellent opportunity to manage complex, unusual medical conditions first hand. Here we report a rare respiratory complication in a young primiparous woman following a very prolonged labour in a remote community hospital in the Northern Territory, Australia.
Case
A 23-year-old Caucasian primiparous woman who was at 40 weeks and 6 days of gestation presented to a remote community health center situated approximately 1000 km from the nearest tertiary care referral hospital for delivery of her first child after spontaneous rupture of membrane. She had an uneventful antenatal history and had no significant past medical or surgical comorbidities and was not on any regular medications. She had a BMI of 25 and had a few years of smoking history (about 10 cigarettes per day).
She was noted to have a very prolonged second stage of labour, lasting for about 3–4 hours. During that time she had been pushing with extreme efforts intermittently for prolonged periods. She was also noticed to have had multiple bouts of vomiting, presumably thought to be secondary to inhalation of medical nitrous oxide and oxygen. A healthy baby boy with a weight of 3.3 kg was delivered via normal vaginal delivery.
Six hours postpartum she complained of chest pain associated with mild dyspnoea and altered voice. Her vital signs were unremarkable and stable. She was examined by the on-call GP/obstetric physician who noted subcutaneous emphysema of the neck and chest on palpation. Her chest was clear with normal breath sounds on both lung fields. The physician also recognised crunching and crackling sound heard over the precordium, synchronous with the heartbeat (Hamman’s sign). A chest radiograph revealed evidence of pneumomediastinum (Fig1). After consulting with the respiratory team at the tertiary referral hospital, she was managed with analgesia, supplemental oxygen and close observation at the community hospital. A repeat chest X-ray 24 hours later showed resolution of the pneumomediastinum, and the patient’s symptoms improved. The subcutaneous emphysema resolved spontaneously after 3 days and she was discharged home. She was followed up by the respiratory team 2 months later with no further complications.
Discussion
Diagnosis of pneumomediastinum can be challenging, especially in remote community hospital settings, given that its most common symptom (chest pain) carries broad differentials1. Clinical skills (physical examination) and decision making on management are extremely important where resources are limited. Awareness of this condition is crucial to differentiate between other conditions with higher morbidity and mortality such as pneumothorax, aortic dissection, oesophageal rupture, pulmonary or amniotic fluid embolism and myocardial infarction. The first report showing the occurrence of pneumomediastinum during labour was published by Simmons and later by Louis Hamman2. Since then about 200 cases have been reported in the literature with an estimated incidence of 1 in 100 000 deliveries2-4. Although the clinical presentation can be dramatic, it is a benign condition with a self-limiting course.
The pathophysiology is thought to be secondary to a significant increase in intrapulmonary pressures, leading to disruption of alveolar walls and entry of air into the pulmonary interstitium. The negative pressure gradient of the mediastinum in relation to the pulmonary parenchyma will naturally cause air to flow into the mediastinum and vents out to the thorax and subcutaneous tissues, thus explaining the clinical signs associated with this condition5. In severe cases, tension pneumomediastinum can occur, which can prove fatal. Fortunately, this is a very rare event.
Management of this condition, unless complicated by tension pneumomediastinum or pneumothorax, is supportive as most cases resolve with conservative management alone. Supplemental oxygen may hasten reabsorption2-4. If detected during labour, steps to avoid repeated maternal expulsive efforts by using maternal forceps or converting to caesarean section under regional anaesthesia may be undertaken. A nitrous oxide and oxygen mix should be avoided as it may lead to expansion of trapped gas2. Recurrence of pneumomediastinum in future pregnancies is not known to be common.
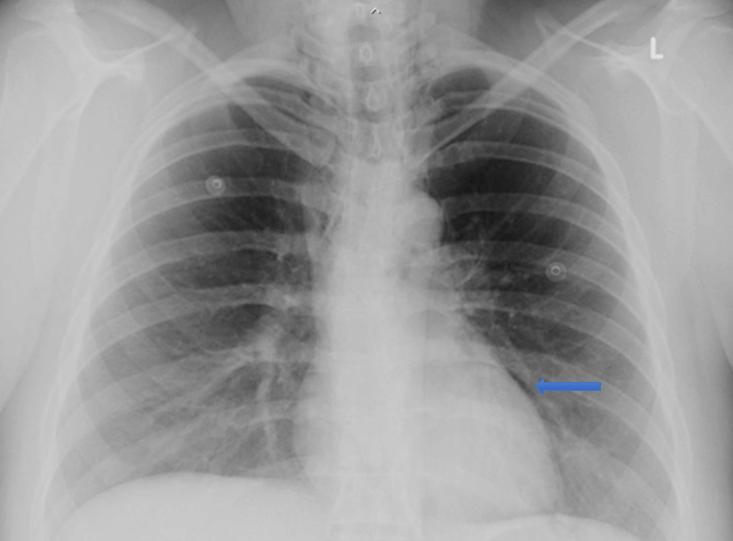 Figure 1: Chest X-ray of the patient, showing pneumomediastinum.
Figure 1: Chest X-ray of the patient, showing pneumomediastinum.
