Introduction
The administrative regions of South Korea consist of about 172 urban areas (city, district) and about 86 rural areas (county). South Korea has a population of approximately 90% in urban areas and 10% in rural areas1. Urban areas have large populations and a high distribution of economic and medical resources.
South Korea has made efforts to reduce the gap of oral health status between urban areas and socioeconomically poor rural areas by executing the free pit and fissure sealing (PFS) program mainly for rural areas during the period 2002–2007 as one of the national oral health programs promoted by the Ministry of Health and Welfare2. PFS began to be covered by the National Health Insurance (NHI) from December 2009 (Table 1).
People need to visit a dental clinic to benefit from NHI coverage of PFS. This means that people living in an area of low dental accessibility may have disparity on benefits of NHI PFS coverage compared to people living in areas with easy access to dental treatment. This study proposed to examine the difference of experience in PFS among children aged 6–14 years before and after the coverage of PFS by NHI, and between urban and rural areas.
Table 1: Changes to criteria for National Health Insurance coverage of oral pit and fissure sealing3, 2009–2013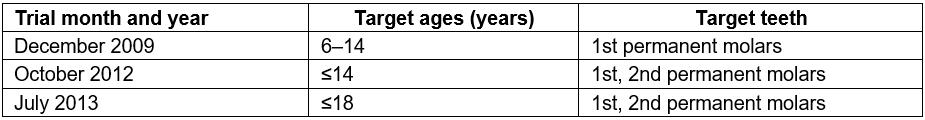
Methods
Data for 2007 and 2012 from the Korean National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey (KNHANES IV, V) and the Korean Statistical Information Service4 were used for this study. KNHANES examines about 10 000 people over the age of 1 year by taking probability samples of 20 households in 192 regions each year. PFS was included in the NHI in December 2009. The KNHANES data year designated as ‘before coverage’ was 2007, and the ‘after coverage’ year was 2012.
This study used the complex sample analysis method. The subject age range was 6–14 years. Areas were classified as either urban or rural. Data were analysed using STATA v13.0 (StataCorp; http://www.stat.com). The number who experienced PFS was calculated by multiplying the population of children aged 6–14 years by the proportion of PFS that derived from sampled survey coverage (Table 2).
Table 2: Characteristics of survey sample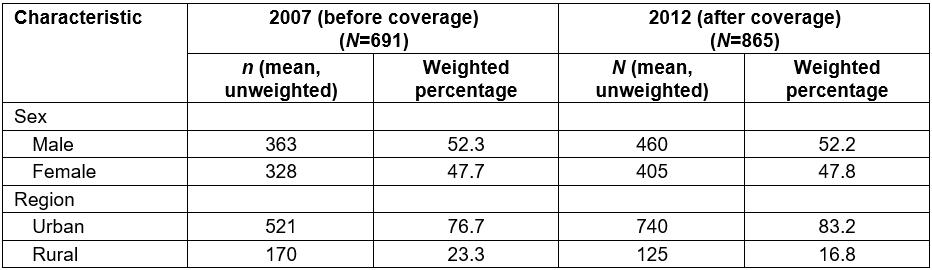
Ethics approval
The Institutional Review Board of the Korea Centers for Disease Control approved the Korean National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey (KNHANES IV, V) (2007-02CON-04-P, 2012-01EXP-01-2C)5.
Results
Reduction of out-of-pocket expense according to NHI coverage PFS experience of children aged 6–14 years increased from 28.7% before coverage to 34.9% after coverage (Fig1). PFS experience of children aged 6–14 years in urban areas increased from 29.2% before coverage to 35.6% after coverage. In rural areas, coverage increased from 27.2% before coverage to 31.5% after coverage. However, after the coverage of PFS by NHI, PFS experience in the rural area is still low and the difference between urban and rural areas increased from 2.0% to 4.1%. The average number of sealed teeth per person in urban areas increased from 0.75 before coverage to 1.16 after coverage. The average number of sealed teeth per person in rural areas increased from 0.64 before coverage to 0.92 after coverage (Fig2).
The number of urban children aged 6–14 years who experienced PFS was estimated as 1 456 399 before coverage and 1 615 785 after coverage. The number of rural children aged 6–14 years was estimated as 28 532 before coverage and 18 423 after coverage (Table 3).
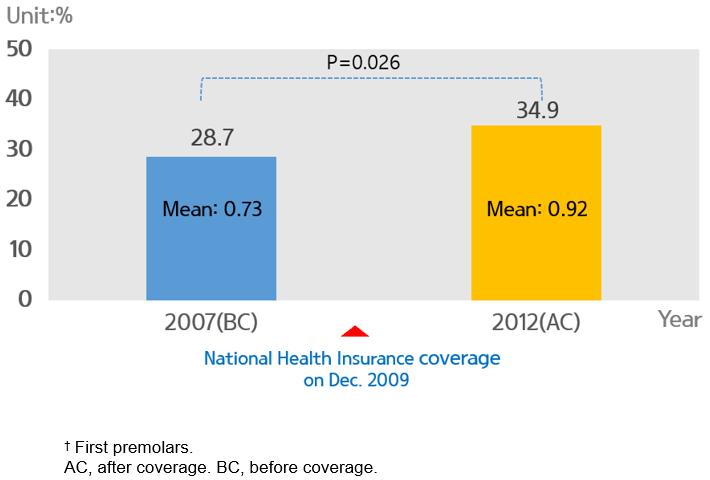 Figure 1: Proportion of population having pit and fissure sealing and mean number of sealed teeth† among Korean children aged 6–14 years, before and after National Health Insurance coverage.
Figure 1: Proportion of population having pit and fissure sealing and mean number of sealed teeth† among Korean children aged 6–14 years, before and after National Health Insurance coverage.
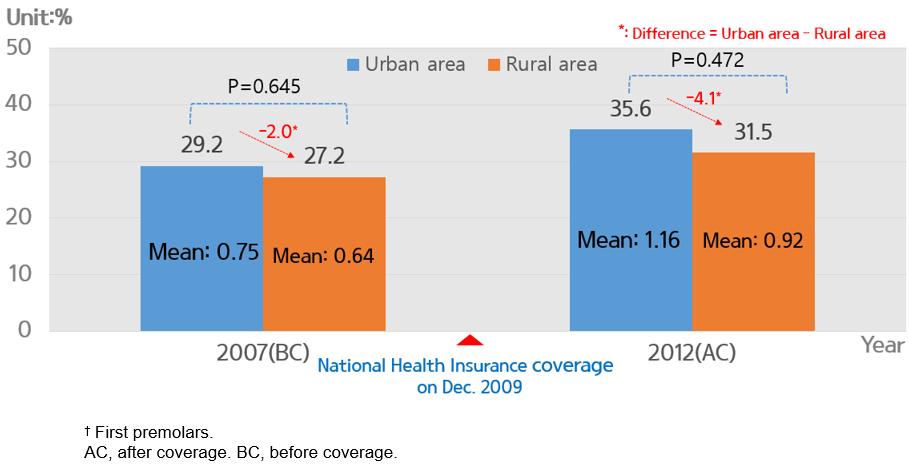 Figure 2: Proportion of urban and rural populations having pit and fissure sealing and mean number of sealed teeth† among Korean children aged 6–14 years, before and after National Health Insurance coverage.
Figure 2: Proportion of urban and rural populations having pit and fissure sealing and mean number of sealed teeth† among Korean children aged 6–14 years, before and after National Health Insurance coverage.
Table 3: Estimated number of people experiencing pit and fissure sealing among Korean children aged 6–14 years, before and after National Health Insurance coverage 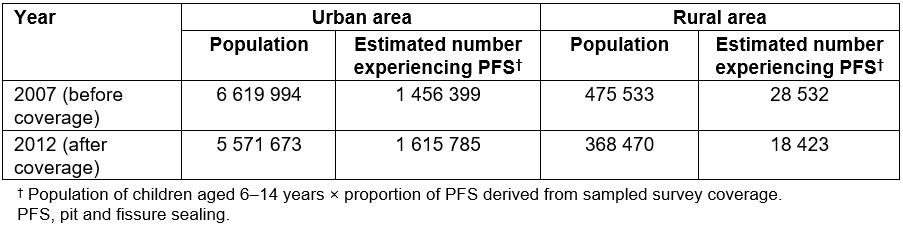
Conclusions
With coverage by NHI, the percentage of beneficiaries and the mean number of sealed teeth per child aged 6–14 years doubled in urban areas, but in rural areas the percentage of beneficiaries increased insignificantly, and the mean number of sealed teeth per person decreased, showing regional inequality.
Covering PFS, which has been provided through public health programs, by NHI can increase the supply of PFS using private resources, but it may cause disparity in supply because of different accessibility to private medical institutions among areas. It has been reported that the regional distribution of a nation’s medical resources does not necessarily reflect the need for medical services, which can result in an unequal use of medical services or access between regions6. Solving this problem requires changes to public health programs and national health insurance schemes. In South Korea, the solution may be raising accessibility of people with low income by reducing or remitting copayments and, at the same time, increasing the supply of PFS in rural areas through school%u2010based oral health programs.

